nalco group
bone, muscle & joint pain physio
BOOK NOW / WHATSAPP ABOUT YOUR PAIN OR INJURY
- NOVENA 10 Sinaran Drive, Novena Medical Center #10-09, Singapore 307506
- TAMPINES 9 Tampines Grande #01-20 Singapore 528735
- SERANGOON 265 Serangoon Central Drive #04-269 Singapore 550265
Home > Blog > Physiotherapy & Hand Therapy > Conditions We Treat > Elbow Pain > Avulsion Fractures Of The Olecranon
avulsion fractures of the olecranon
Olecranon fractures
Avulsion olecranon fractures typically occur with elbow disorders and they’re often regarded as extra-articular fractures.
Unfortunately these type of fractures are generally associated with hematomas and joint effusions. It’s also worth noting that the operative and physiotherapy treatments for this type of fracture are quite straightforward (which is a good thing).
In this article, we’ll take an in-depth look at avulsion fractures of the olecranon, what causes them, some common symptoms to watch out for and a few recommended treatment options that you should know about.
What Are Avulsion Fractures of the Olecranon?
The human elbow joint is held together by tendons, muscle, and ligaments and it’s made up of three core bones –
- radius
- ulna and
- humerus
An olecranon fracture is basically a break that occurs in the pointy bone located at the end of the ulna that becomes noticeable whenever you bend your elbow.
Olecranon fractures are typically an isolated injury and it’s more common than what people think. That being said, it may also occur as part of a complex elbow disorder or injury.
Note: Any injuries that may coexist with olecranon fractures usually affect other regions of the same upper extremity.
You should also note that most olecranon fractures have a risk and tendency to become widely separated due to the pull of triceps insertion and for such cases its unfortunate but they will likely require operative treatment.
Unstable or severe cases of such fractures are typically associated with trauma and they can be pretty complex and difficult to treat.
The type of fracture can be classified as either
- stable and nondisplaced or
- unstable and displaced
Avulsion fractures are known to be unstable fractures because the triceps mechanism gets disrupted. They often necessitate a procedure where the triceps are repaired back down to the olecranon.
but What Causes Fractures of the Olecranon?
Fractures of the olecranon may occur as a result of a direct blow to the elbow when it’s at 90 degrees of flexion or due to forced elbow hyperextension.
Avulsion injuries tend to occur due to eccentric or excessive contraction of the triceps tendon and they usually have an oblique or transverse fracture line. They occur more frequently in patients with osteoporosis.
It’s also observed that even after the best rehabilitative care, most patients may experience loss of some elbow extension as a permanent side-effect of the olecranon fracture (called as "extensor lag").
In addition to a direct blow, some other causes of this type of fracture may include:
- Falling directly on the elbow
- Falling with the elbow flexed on an outstretched hand (indirect trauma)
- Triceps bony avulsion (a rare injury)
- Stress fractures (tiny cracks in a bone that are common in gymnasts and throwing athletes)
It’s important to mention that suffering from a nerve injury can further complicate fractures of the olecranon.
Olecranon Fracture Symptoms to Look Out For
Patients with olecranon fractures typically experience swelling and elbow pain soon after a fall.
In cases where the fracture is classified as displaced, there may be an obvious deformity with a visible gap at the elbow. Moreover, one of the first signs of an olecranon fracture is the loss of ability to extend or straighten the elbow against gravity.
If you have developed an olecranon fracture, you may experience a sudden sharp and intense pain at the time of injury, which may cause you to cradle your affected arm to protect it. This type of pain typically occurs at the back of the elbow and may settle into a dull ache that becomes more pronounced around nighttime or early morning.
You may also experience bruising and pain when you firmly touch the injured region of your elbow.
Certain movements of the elbow, shoulder, or wrist or certain activities may increase the pain and it may also become more prominent with contracting of the triceps muscle or stretching. In some cases, pins and needles or some form of numbness can also be experienced in the forearm, hand, or the elbow.
Moreover, patients with olecranon fractures may also experience tenderness to touch and pain while moving the elbow joint. If you ignore these symptoms, you’re likely to cause even more damage, delay the healing or recovery process or prevent the fracture from healing at all.
Who’s More at Risk?

The majority of olecranon fractures occurs in people who are 50 years of age or older.
Younger patients with this type of fracture tend to have injuries that are associated with a higher energy injury mechanism such as
- sports
- motor vehicle accidents (road traffic accidents)
These fractures make up around 10 percent of all fractures that affect the upper extremity and the incidence happens to be 12 per 10,000. The average age of people with olecranon fractures is 57 and men are more likely to develop an injury when they’re young as opposed to women.
Gymnasts and wrestlers who perform isometric exercises regularly or anyone involved in weight-bearing activities are more at risk of sustaining fractures of the olecranon.
Other Injuries That Are Similar
It’s advisable for the doctors to rule out other injuries of the elbow when they’re coming up with a treatment plan for the patients.
This includes evaluating the patient’s skin for open fractures.
Some common injuries that are frequently associated with olecranon fractures include
- neck and radial head fractures
- coronoid fractures
- collateral ligament
injuries and
- radial head dislocation
what are the Treatments for olecranon avulsion fractures?
An in-depth subjective and objective assessment from an experienced doctor or physiotherapist is necessary to diagnose avulsion fractures of the olecranon.
Furthermore, an X-ray is also needed to confirm a diagnosis.
In some cases, additional investigative procedures like CT scan, MRI or bone scan, may be necessary to help with diagnosis and determine the severity of the fractures.
Typically, there are two forms of treatment for olecranon fractures depending on the joint involvement, displacement, and the fracture pattern.
Olecranon Fracture Conservative Treatment
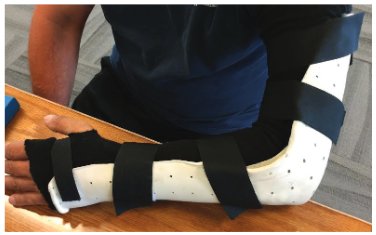
For patients who have sustained stable olecranon fractures, a sling or a customized elbow splint is generally used to provide support to the elbow and keep it in place while it heals.
The orthopedic doctor will closely monitor the healing process of the fracture and may ask the patient to get X-rays done.
If the fracture isn’t out of place, the patient may be allowed to start moving the elbow after a couple of weeks with the guided assistance of our principal hand therapist and/or principal physiotherapist.
However, patients are strictly advised against performing weight-bearing or lifting exercises, at least for several weeks.
Due to the prolonged splinting time, the patient’s elbow may become quite stiff and a longer period of therapy may be required after the cast is removed to restore movement.
Olecranon Fracture Surgery
In cases where the fracture is open (bone is visible through the skin) or it’s displaced, surgical treatment becomes necessary.
It’s usually performed after making an incision at the back of the elbow through which the fractures can be fully accessed. The broken pieces are then put together and kept in place using plates and screws, or pins and wires.
Patients who sustain unstable olecranon fractures should consult with an orthopedic surgeon within 24 hours following the injury. These types of injuries need to be kept in a long-arm splint to control the swelling and relieve discomfort. Not only that, open fractures and dislocations also require immediate consultation.
For unstable and displaced olecranon fractures, internal fixation construct happens to be the recommended treatment option. Suture anchors or drill holes in the olecranon are used to repair the triceps down to the bone. Additionally, some unstable intra-articular fractures need to be treated with open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF).
Generally, a posterior splint is used for around 7-10 days to let the soft tissues heal completely and the duration of immobilization varies, depending on the patient’s age, health, osseous status, desired goals as well as healing response. When the splint is finally removed, unlimited passive movement may be started.
Even though elbow flexion and active forearm supination and pronation are allowed, it’s advisable to avoid active extension for at least six weeks. It’s important to consider that full motion in all different directions is typically achieved by the end of six weeks (but note that this can be delayed up to 12 or more weeks depending on the patient's healing condition and compliance). Strengthening exercises of the wrist and elbow and gentle active extension may be started around 8 weeks or later, depending on the stability and healing rate of the olecranon fracture.
Just like other fractures involving the elbow, electrical stimulation and cryotherapy can be used to alleviate pain and reduce swelling. Nerve glides must be used whenever possible and scar massage should also begin at two weeks.
Early movement is expected to begin right after surgery, and it should be assisted with either occupational therapy or physiotherapy management.
hand therapy and Physiotherapy Management
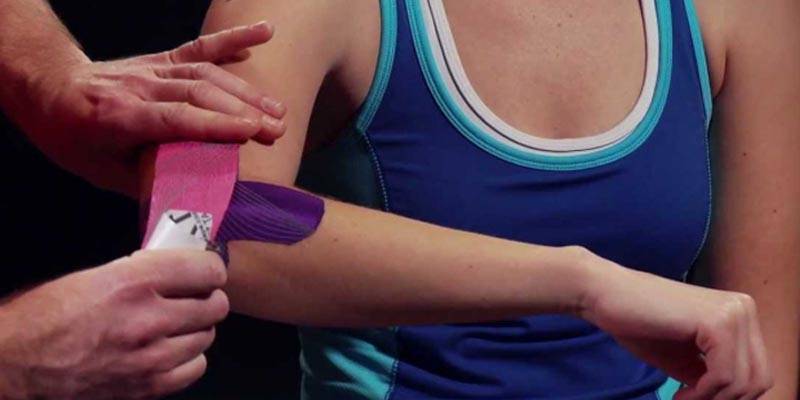
There’s no denying the importance of appropriate post-operative care for maximum healing - like we often tell our patients, there are generally 3 components to healing 100%
- patient's internal healing rate and compliance
- doctor's skills, knowledge and ability
- high quality physiotherapy and hand therapy intervention
Our principal hand therapists and physiotherapist’s primary goal is to help restore the patient’s range of motion and normalize daily activities.
As far as olecranon fractures are involved, bone healing and rehabilitation may take around 12 weeks.
Patients are also advised to perform flexibility and strengthening exercises because strength and soft tissue flexibility are often lost with disuse and immobilization.
Hand therapy and physiotherapy management may include the following:
- Joint mobilization / range-of-motion
- Muscle strengthening
- Bracing or taping
- Electrotherapy
- Soft tissue massage
- Activity medication techniques
