nalco group
bone, muscle & joint pain physio
BOOK NOW / WHATSAPP ABOUT YOUR PAIN OR INJURY
- ORCHARD 400 Orchard Road #12-12 Singapore 238875
- TAMPINES 9 Tampines Grande #01-20 Singapore 528735
- SERANGOON 265 Serangoon Central Drive #04-269 Singapore 550265
Home > Blog > Physiotherapy & Hand Therapy > Conditions We Treat & Hand Conditions > Elbow Pain > Osteoarthritis Radio Humeral Joint Elbow Physiotherapy
Osteoarthritis Radio Humeral Joint elbow physiotherapy

Whether you’re a baseball player or a home maker or active executive, your elbow joint will play a vital role in your day-to- day activities. Elbow pain can not only be quite bothersome, but it can also hinder you from doing some of the things that you love doing.
Elbow osteoarthritis refers to an elbow disorder that’s typically characterized by
- stiffness in the elbow
- limited
range of movement and
- impingement pain.
Nonoperative management can help relieve pain and improve function and if that doesn’t work, surgical intervention may become necessary (but we typically try to help patients to prevent invasive surgeries).
In this article, you’ll learn all you need to know about elbow osteoarthritis, some of its many causes and symptoms, and surgical and nonsurgical treatment options that your doctor may consider.
What Happens in Osteoarthritis of the Elbow?
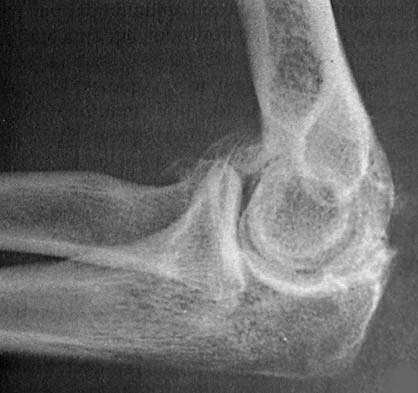
Osteoarthritis of the elbow is when the cartilage surface of the elbow gets damaged or worn out.
This may occur due to a previous injury like an elbow fracture or elbow dislocation, but it’s most of the time it's mainly the result of a regular wear-and-tear away of the joint cartilage from overuse and age.
That being said, it’s worth noting that osteoarthritis generally affects the weight-bearing joints like the knee and hip, and the elbow is actually one of the least affected joints due to its strong stabilizing ligaments that can tolerate eccentric forces and well-matched joint surfaces that prevent it from becoming unstable.
first of all, What Causes Elbow Osteoarthritis?
Trauma happens to be a predominant cause of elbow osteoarthritis.
Any trauma that’s inflicted on the elbow joint can potentially result in post-traumatic osteoarthritis, which can cause the articular surfaces to become incongruent or lead to elbow instability.
Most patients of elbow OA report pain as well as a grating sound or sensation while flexing and extending their arms or rotating their forearms. Some patients also have a history of elbow injuries, like an elbow dislocation or a fracture that involves the surface of the joint.
Some common risk factors for osteoarthritis of the elbow include:
- Loss of joint cartilage
- Surgery is required to repair an injury to the elbow or reconstruct the joint
- It’s not possible to reconstruct or restore the joint surface to its pre-injury condition
Additionally, an injury to the ligaments that leads to instability can also cause elbow osteoarthritis, even when the surface of the elbow isn’t damaged. This is because the normal forces exerted along the elbow have changed which can cause the joint to get worn out faster.
It’s also important to consider that for some patients, no single injury occurs to the elbow. Instead, it’s the result of work-related or outside activities where the patient ends up placing more demands on their elbow joint than it can tolerate.
For instance, professional baseball players inflict unusually large forces across their throwing elbows which can eventually cause the stabilizing ligaments to fail.
Of course it goes without saying that the easiest and most effective way you can reduce your chances of having elbow osteoarthritis is by avoiding injuries to your elbow joint. But even if you aren’t able to prevent them, it’s advisable to get them checked and treated right away.
Moreover, any individuals who are involved in work or sports activities that require muscular strength around the elbow should utilize appropriate conditioning and elbow joint mobilization techniques.
Common Symptoms of radio-humeral joint elbow osteoarthritis
Patients with osteoarthritis of the elbow may experience a variety of symptoms, and some of them may occur more frequently than others.
Here’s a list of some common symptoms that are associated with elbow radio-humeral osteoarthritis:
- Difficulty while moving the elbow joint
- Elbow stiffness
- Joint instability
- Joint pain
- Bone scraping or grating
- Locking sensation in the elbow
- Bone spurs
- Joint swelling
- Limited range of movement
It’s worth mentioning that both pain and loss of range of movement may not happen at the same time.
Bone grating is caused by damaged or wearing out of the cartilage, resulting in the loss of the smooth joint surface. The ‘locking’ sensation, on the other hand, is a result of loose pieces of bone or cartilage that dislodge from the joint and get trapped between the moving joint surfaces.
Joint swelling generally doesn’t happen at first and only occurs as the disease progresses.
In the later stages of elbow OA, patients may experience a strange numbness in their small finger and ring finger which occurs due to elbow swelling or functional limitation.
Joint swelling can end up putting pressure on the nerve and causing a tingling sensation as well. Some common red flags to look out for include septic arthritis as well as any infections that are associated with surgery.
Who’s More at Risk of getting elbow osteoarthritis?

You may not know this, but osteoarthritis is basically one of the most common causes of disability in older people.
Even though almost anyone can develop osteoarthritis of the elbow, but some people have a higher chance based on their habits, lifestyle, and line of work.
People who are more at risk of developing elbow osteoarthritis include:
- Older adults
- People with family members who have osteoarthritis
- People with a history of elbow fracture or injury
- Middle-aged males who perform manual labor like hammering and shoveling regularly
- Overhead throwing athletes
- People who work with pneumatic tools
- Weightlifters
- People who are dependent on crutches or wheelchairs
Moreover, primary osteoarthritis of the elbow is four times more likely to affect men as opposed to women with an average age of onset of fifty years.
Post-traumatic osteoarthritis of the elbow can occur in people of any age or gender, but it’s more common in young men (this is mainly because they are more at risk for trauma and sports-related injuries be it sports, motorvehicle accidents etc).
Whether or not you have a risk of developing elbow OA after injury depends on the pattern as well as the intensity of the injury.
Other Conditions That Are Similar to Elbow Osteoarthritis
Before diagnosing elbow osteoarthritis, a clinician should try to determine any changes in hand function, weakness, neuropathic pain, or any changes to sensation. This is because ulnar neuropathy and cubital tunnel syndrome are often associated with elbow OA.
Differential diagnoses may include:
- Lateral epicondyle tendinopathy
- Ligament sprain/rupture such as elbow medial collateral ligament or elbow lateral collateral ligaments
- Medial epicondyle tendinopathy
- Referred pain from cervical spine
- Undiagnosed elbow fracture
Osteoarthritis Elbow Treatments
If you suspect that you may have developed osteoarthritis of the elbow, your doctor may diagnose it based on your symptoms as well as standard x-rays (that show arthritic changes). Advanced diagnostic imaging like MRI and CT aren’t usually necessary to diagnose elbow OA.
Pain management often involves taking the patient’s age, activity level, treatment history, and disease severity into consideration. The options of treatment may vary depending on what the patient desires, their overall health condition, and the results of x-rays and tests performed.
Nonsurgical Treatment
For patients who are in their early stages of elbow osteoarthritis, the most common form of treatment is nonsurgical which may involve oral medicines to
- reduce pain
- activity modification and
- elbow physiotherapy & hand therapy
Injections
In some instances, corticosteroid injections (also known as H&L injections) are also used to treat the symptoms because it may prove effective for some patients. Even though the effects of these injections aren’t permanent, they may provide pain relief.
There is also PRP injections, which are "platelet-rich-plasma" injections that patients can consider. This is very natural, as the platelet-rich-plasma is taken from your own blood, and extracting it via centrifuge spinning.
We can recommend doctors to you who can do these injections well - contact us and we'd be happy to guide you.
Surgical Treatment
In cases where nonsurgical treatment doesn’t prevent the symptoms from worsening, surgical intervention may become necessary. It’s important to note that by the time elbow osteoarthritic can be observed on x-rays, there’s already been significant damage to the joint surfaces. Fortunately, even if the bone spurs or damage is quite severe, arthroscopy can be considered which happens to be a minimally invasive surgical procedure.
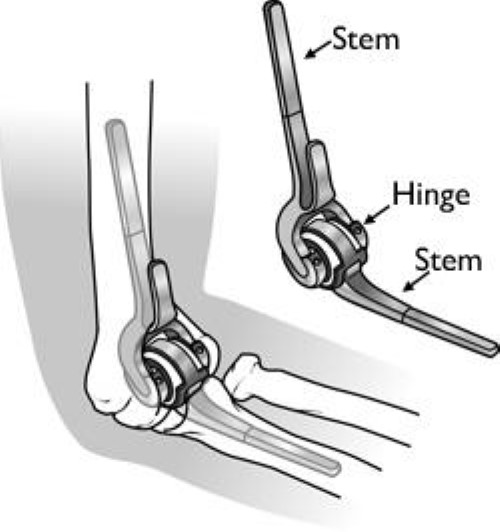
It’s been found that arthroscopy doesn’t only help control the symptoms, but also improves the patient’s range of movement. It attempts to eliminate bone spurs and smooth out irregular joint surfaces. It may be performed as an outpatient treatment and recovery is understandably quick.
If the patient’s joint surface has worn away completely, elbow joint replacement can help bring about relief. There’s a variety of elbow joint replacement available and the improvement in function and pain has been found to be dramatic in selected patients.
For patients who are too active or too young to undergo joint replacement, doctors may consider other surgical treatment options. If loss of movement happens to be the primary symptom, it may be advisable for the doctor to smooth out the joint surface in order to release the stiffness.
In some cases, a new surface can be made using the patient’s body tissues which may show significant improvements in function and symptoms.
We can recommend doctors to you who can do total elbow arthroplasty / replacements - contact us and we'd be happy to guide you.
Elbow Osteoarthritis Physical Therapy
Needless to say, getting treated by our principal hand therapists and/or principal physiotherapists can be quite effective in
- alleviating elbow pain
- improving range of motion
- rebuilding elbow strength and power
There are also some gentle osteoarthritis elbow exercises that patients can try out as well as heat or cold therapy to reduce pain. It’s highly recommended that patients limit or modify their activities that might irritate their elbow further or exacerbate the symptoms.
During the first few appointments, our therapists will focus on pain management and utilizing modalities like
- cold therapy
- heat therapy
- gentle manual therapy
- gentle range of motion exercises / stretching
- gentle ultrasound therapy to accelerate soft tissue healing
- etc
to help decrease any pain or swelling you may be experiencing at the shoulder, around your elbow, in your hand, or along your forearm.
