nalco group
bone, muscle & joint pain physio
BOOK NOW / WHATSAPP ABOUT YOUR PAIN OR INJURY
- ORCHARD 400 Orchard Road #12-12 Singapore 238875
- TAMPINES 9 Tampines Grande #01-20 Singapore 528735
- SERANGOON 265 Serangoon Central Drive #04-269 Singapore 550265
Home > Blog > Spinal Physiotherapy > What Is Sciatica?
What Is Sciatica?
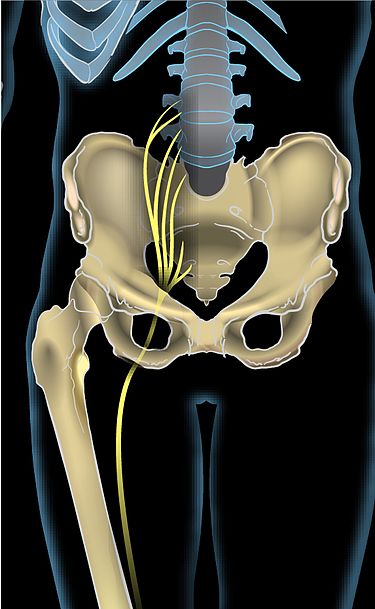
Our sciatic nerve is the largest and longest nerve in our body with a width of almost 2 cm. The sciatic nerve starts at/from our sacral plexus (which is a bundle/network of nerves inside our pelvic area, that then branches out and downwards into each thigh and leg).
Our sciatic nerve has two key functions:
- Motor (movement)
- Sensory (feeling/sensation)
If/when our sciatic nerve is compressed or injured, the symptoms are referred to as "sciatica" ie of sciatic nerve. Patients with sciatica may report experiencing:
- Motor issues: weakness, poor coordination, slow reflexes
- Sensory isses: numbness, electrical sensation, pins and needles etc
first of all, WHAT CAUSES SCIATICA?
The most commonly known reason and cause is the "slipped disc" (medically termed as herniated disc/disc herniation). What happens is that the displaced disc protudes outside of its normal boundaries and presses onto the spinal nerve root that is connected to the sciatic nerve.
And unfortunately, as our sciatic nerve IS the longest nerve in our body, it becomes the most at risk for it to be compressed/damaged. Examples include:
- Spinal stenosis, where the spinal canal tightens/narrows and causing symptoms that resemble sciatica. This canal narrowing can be caused by both spine arthritis and spinal disc issues.
- Piriformis syndrome happens when the piriformis muscle can be inflamed. Our piriformis is the muscle that is found deep in our gluteus (butt muscle) and is located on top of the sciatic nerve as the nerve exits the spine and goes down/into your leg. When this muscle is inflamed, it swells and this can protude/press onto the sciatic nerve, causing sciatica-like symptoms.
There are other conditions that may also cause sciatica-like symptoms, for example:
- Lumbar facet joint syndrome refers to pain that is found/caused from the joints inside the back (spinal vertebrae) which can cause both back discomfort as well as symptoms of sciatica.
- Ilio-lumbar syndrome is the inflammation as result of micro-tear/injury of the ilio-lumbar ligament (ligament that connects the ileum and the lumbar, at the back of the pelvis).
- sacro-iliitis refers to an inflammation of the sacro-iliac joint, which can be caused by trauma or arthritis.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS of sciatica?
Patients with sciatica may experience one or more of the following:
- Tingling or burning sensation at the back of the thigh or front/down of the leg
- Constant pain at one side of the thigh/buttock
- Pain the the thigh or butt that is aggravated with sitting/prolonged sitting
- Weakness, difficulty coordinating or moving the knee, leg and foot
- Shooting pain that travels down from the butt to the thigh
In some rare/severe cases, if there is very severe pain AND difficulty controlling bowel or bladder, it is considered as a medical emergency and patients need to immediately get treated/seen by a spine specialist or orthopedic surgeon.
TREATMENT for sciatica
Sciatica is a specific type of nerve injury, pain and symptoms which is caused and aggravated both by
- pressure/compression
- inflammation
on the spinal nerve root, so the treatments for sciatica will be focused on relieving both of the issues as mentioned above. Treatments will include:
- Spinal physiotherapy which will provide a combination of treatment modalities such as manual therapy, ultrasound therapy to accelerate soft tissue healing, computerized spinal decompression traction, mobilization etc
- Medical/medication such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or even oral steroids to bring down the inflammation, pain, swelling and stiffness.
- In severe cases, patients may consider surgical interventions such as laminectory if the severe sciatic pain doesn't resolve with physiotherapy and/or if there is bladder/bowel dysfunction.
When patient's sciatica has been resolved, they may benefit from an ongoing spinal care, including spinal physiotherapy and clinical pilates to ensure that their core and back muscle strength are in tip top condition, and ensure flexibility in joints.
